From Paper to Tokens: Transforming Legislative Services in the Chamber of Deputies of Chile
Written in September, 2024
This publication is part of the book “Artificial Intelligence in Legislative Services: Principles for Effective Implementation”. To download the entire book, use the button below:
Acknowledgements
The modernisation of the Chamber of Deputies of Chile through the CAMINAR project required remarkable dedication, coordination, and expertise across multiple areas to bring this innovative vision to fruition. I would like to recognise Mr. Miguel Landeros, Secretary-General of the Chamber of Deputies of Chile, Mr. Luis Rojas, Deputy Secretary-General, Mr. Hernan Figueroa, IT Director, Mr. Esteban Sánchez Rivera, Head of Information Systems Development, Ms. Virginia Carmona, Deputy Director of Parliamentary Assignments, and all their staff for their unwavering leadership, technical expertise, and commitment throughout the development of CAMINAR. Their collective efforts were crucial in transforming the Chamber's legislative and administrative processes.
I. Introduction
The Chamber of Deputies of Chile has undergone a significant transformation in recent years, moving from a largely paper-based legislative process to a fully digital system. This shift was driven by the need to address inefficiencies in document management, information retrieval, and legislative transparency. The latest stage of this transformation came in the form of the CAMINAR project, a comprehensive Artificial Intelligence initiative designed to modernise both legislative and administrative functions within the Chamber of Deputies.
CAMINAR introduced advanced artificial intelligence and digital tools aimed at streamlining key processes. Modules like CAMINAR-L, focused on legislative tasks, and CAMINAR-A, addressing administrative needs, have significantly enhanced the Chamber's ability to manage legal texts, financial oversight, and parliamentary assignments. By transitioning to a paperless workflow and embracing AI-powered solutions, the Chamber has improved efficiency, transparency, and accountability in its operations.
The following sections provide an in-depth exploration of this transformation, detailing the challenges faced by the Chamber, the development and implementation of CAMINAR, and the resulting impact on legislative and administrative functions.
II. Background
The Chamber of Deputies of Chile has encountered a multitude of challenges over the years, driven by both historical events and evolving demands for legislative efficiency and transparency. Historically, the Chamber operated in a predominantly analogue environment where legislative activities were heavily reliant on paper documents, face-to-face interactions, and traditional methods of information management. This setup, while functional in earlier times, became increasingly inefficient and cumbersome in the face of rapid technological advancements and the growing complexity of legislative work.
Throughout much of the 20th century, the Chamber's operations were characterised by manual record-keeping and limited technological integration. This not only slowed down the legislative process and administration but also made it difficult to manage and retrieve information promptly. The need for more efficient processes became particularly apparent during periods of intense political activity and reform, where the volume of legislative work increased significantly.
The advent of the digital age brought about new expectations for efficiency. The public and Members of Congress began to demand greater insight into legislative processes and quicker access to information. Additionally, the complexity of modern governance required more sophisticated tools to handle the vast amounts of data generated by legislative activities.
An important moment highlighting the need for digital transformation was the COVID-19 pandemic. The pandemic disrupted traditional legislative procedures and administration, necessitating a swift adaptation to remote work. This sudden shift underscored the Chamber's technological shortcomings and the urgent need for a more robust digital infrastructure. The inability to conduct business as usual due to lockdowns and social distancing measures forced the Chamber to reconsider its reliance on physical documents and in-person interactions.
The need for a comprehensive digital transformation became undeniable. The Chamber of Deputies responded to this need by investing in a robust digital infrastructure, establishing a paperless workflow, and embracing a digital-first approach to legislative and administrative processes. The institution required a solution that would not only modernise its legislative process and administration but also enhance efficiency. This is where the CAMINAR project, and specifically CAMINAR-L and CAMINAR-A, comes into play.
As Esteban Sánchez Rivera, Head of Information Systems Development at the Chamber of Deputies of Chile, noted, "The AI projects have been the result of the Chamber of Deputies' constant trajectory in the search for implementing innovative, efficient, and useful technological tools that benefit the parliament, the parliamentarians, and the citizens."
CAMINAR-L (Legislative) is designed to address these needs by leveraging advanced digital technologies and artificial intelligence to streamline legislative processes. One of the core components of CAMINAR-L is the use of vectorised legal databases. These databases allow for the precise and efficient management of legal texts, ensuring that data is both accurate and easily retrievable. By vectorising the legal databases, the Chamber can quickly access relevant information, reducing the time and effort required to sift through vast amounts of legislative documents.
Another critical aspect of CAMINAR-L is human validation. While AI and digital tools can significantly enhance efficiency, the accuracy and reliability of legislative work still require human oversight. By integrating human validation into the process, CAMINAR-L ensures that the outputs generated by AI tools are checked for errors and relevance, maintaining the integrity of the legislative process.
Bias regulation is also a fundamental principle guiding CAMINAR-L. In legislative work, the presence of bias can significantly impact the outcomes and fairness of the process. CAMINAR-L incorporates mechanisms to modulate and reduce bias, ensuring that the AI tools used provide balanced and impartial support to Members of Congress.
The concept of normative hierarchy is crucial in the legislative context, where different laws and regulations hold varying degrees of importance. CAMINAR-L prioritises the most significant legal norms in its responses, ensuring that the advice and information provided to Members of Congress reflect the correct legal framework and hierarchies.
By addressing these core needs—efficient information management, reliable human oversight, bias regulation, and respect for normative hierarchies—CAMINAR-L transforms the legislative process within the Chilean Chamber of Deputies. It empowers Members of Congress with tools that enhance their ability to draft, debate, and pass legislation in a manner that is both timely and informed.
Complementing CAMINAR-L, CAMINAR-A (Administrative) is focused on modernising the Chamber’s administrative functions, particularly those related to the management of parliamentary assignments and financial oversight. CAMINAR-A leverages artificial intelligence to automate and enhance various aspects of administrative processes, ensuring that parliamentary resources are allocated and utilised in compliance with the stringent regulations governing public funds.
Through CAMINAR-A, the Chamber has implemented tools that allow for real-time access to financial data, automatic extraction and validation of receipt information, and clear guidance on the complex regulatory frameworks surrounding parliamentary expenses. This ensures that all expenditures are managed efficiently, with a high degree of transparency and accountability. By automating these processes, CAMINAR-A not only reduces the administrative burden on staff but also mitigates the risk of errors, thereby strengthening the Chamber’s overall governance.
CAMINAR is not a static solution but a continuously evolving project aimed at continually adapting to the changing needs of the legislative activities and incorporating new advancements in artificial intelligence and additional legislative databases. Additionally, the Chamber is exploring the creation of a public-facing version of CAMINAR, known as CAMINAR-T, which would provide citizens with access to these powerful tools, further democratising the legislative process.
Together, CAMINAR-L and CAMINAR-A represent a comprehensive approach to modernising the Chamber of Deputies of Chile. While CAMINAR-L focuses on enhancing the legislative process through advanced digital tools, CAMINAR-A ensures that the administrative side of parliamentary work is conducted with the same level of efficiency and transparency.
III. CAMINAR-L
CAMINAR-L1: Transcription Assistant
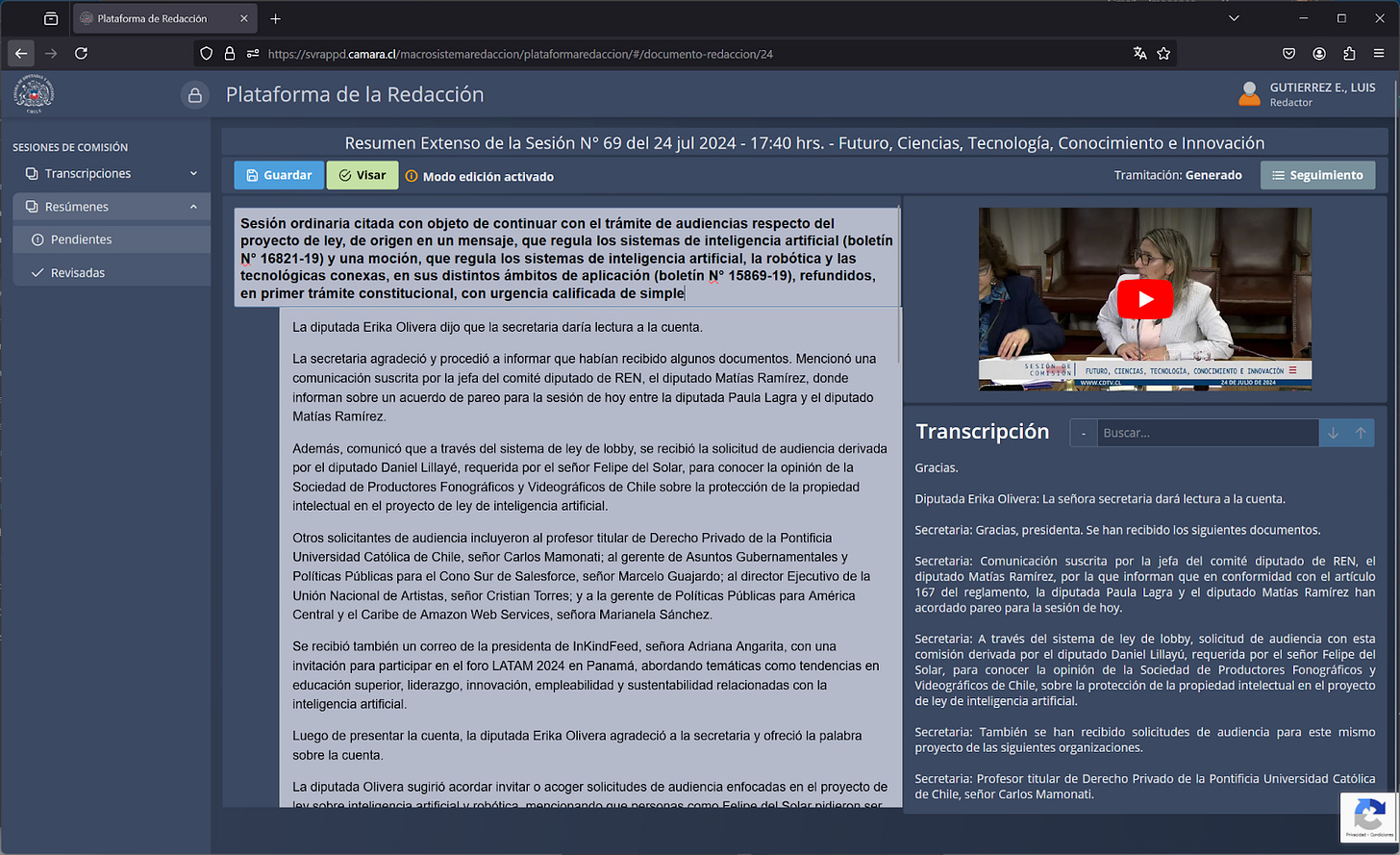
The CAMINAR-L1 module is a component of Project CAMINAR, designed specifically to automate the transcription of parliamentary debates. This innovation addresses the need for efficient, accurate, and timely documentation of legislative proceedings.
Image 1: CAMINAR-L1
The primary objective of CAMINAR-L1 is to facilitate the automatic transcription of parliamentary debates. The integration of Whisper in CAMINAR-L1 facilitates two distinct and independent transcription processes. The online transcription process is used to insert subtitles into the streaming signals of plenary and commission sessions in real-time, ensuring accessibility during live broadcasts. Meanwhile, the offline transcription process generates literal transcriptions of the debates, which are later used as key inputs for the creation of the Diario de Sesiones. This offline process relies on Whisper's AI capabilities to produce accurate, detailed records of the parliamentary debates.
By leveraging advanced speech recognition technologies, this module captures spoken words in real-time, converting them into text. This automation significantly reduces the dependency on manual transcription, which is not only time-consuming but also prone to human error. Leveraging advanced speech recognition technologies like OpenAI's Whisper model, CAMINAR-L1 provides real-time transcription and AI-powered summaries of parliamentary debates, significantly enhancing the efficiency and accessibility of these records.
CAMINAR-L1 is equipped with robust features that enhance its functionality. The real-time transcription feature ensures that every word spoken in parliamentary sessions is captured instantaneously, allowing for immediate access and review. This capability is crucial for maintaining an accurate and up-to-date record of legislative activities.
Another significant feature of CAMINAR-L1 is its ability to generate summaries of the debates. These summaries are powered by AI algorithms, which are based on the depurated literal transcriptions processed by stenographers. After these transcriptions are cleaned and verified, the language model is used to produce concise summaries of committee sessions. This ensures that the summaries maintain a high level of accuracy and relevance, aiding in the efficient documentation of parliamentary activities. These summaries provide a concise overview of the discussions, making it easier for Members of Congress, researchers, and the public to understand the key points and decisions made during the sessions. This feature not only saves time but also enhances the accessibility of the legislative process.
In terms of usage, CAMINAR-L1 is utilised extensively in both plenary sessions and commissions. Its deployment across these settings ensures that the transcription and summarization processes are consistent and comprehensive. By integrating CAMINAR-L1 into these legislative environments, the Chilean Congress can maintain a high standard of documentation. By streamlining these tasks, CAMINAR-L1 allows legislative staff to focus on more strategic and analytical aspects of their work, thereby improving overall productivity and effectiveness.
CAMINAR-L1 also represents a significant stride in the modernization of the Chilean Congress. The project emerged as an innovative solution to the challenges faced by the legislative body, emphasising the importance of digital tools in maintaining legislative functions efficiently. The collaboration between the Senate, the Chamber of Deputies, and the Library of Congress has been crucial in this modernization process, enabling the integration of comprehensive legal databases essential for the effective functioning of CAMINAR-L1 and other modules within the project.
CAMINAR-L2: Semantic Search Assistant
The CAMINAR-L2 module serves as a sophisticated tool designed to enhance the efficiency and accuracy of legal research within the Chilean Chamber of Deputies. This module's primary purpose is to facilitate semantic searches across extensive legal databases, significantly aiding Members of Congress in their quest to find relevant legal precedents and regulations. The system’s ability to comprehend context and meaning in semantic searches is rooted in the vectorisation of the legal database. By using the XML versions of Chile's legal framework, the vectorisation process was refined to the level of the legislative clause, providing a minimum useful detail for semantic understanding. Unlike traditional keyword-based searches, semantic search technology comprehends the context and meaning behind queries, thereby delivering more pertinent and precise results.
This capability is crucial in the legal domain, where the exact phrasing of legislation and precedents can have profound implications. The features of CAMINAR-L2 include advanced search algorithms that utilise natural language processing (NLP) to interpret and respond to queries in a contextually appropriate manner. To improve searches in the vectorised databases, hybrid processes were implemented, integrating semantic searches with keyword-based searches. This means that the system does not merely look for keywords but understands the context in which the words are used, providing results that are significantly more aligned with the user’s intent. This context-based approach is particularly beneficial in legislative research, where the precise interpretation of laws and regulations is critical. One of the key challenges in implementing semantic search within the legal context was ensuring that the system properly understood the hierarchy of the legal norms. Establishing this hierarchy allowed CAMINAR-L2 to deliver coherent and relevant results, prioritising constitutional laws, statutory laws, and regulatory norms appropriately in response to user queries.
In terms of usage, CAMINAR-L2 is employed extensively in both the plenary sessions and the various commissions within the Congress. Members of Congress often need to reference previous laws, amendments, and related legal texts to draft new legislation or to support their arguments in debates. CAMINAR-L2 facilitates this by providing comprehensive search results that include relevant legal texts, historical legislative documents, and pertinent legal precedents. This not only saves time but also ensures that the legislative work is grounded in robust legal research. By enabling precise and contextually relevant searches, the module significantly enhances the accessibility of the legislative process. Members of Congress can base their decisions and legislative drafts on comprehensive and precise legal information, thereby improving the quality and relevance of the laws being crafted.
CAMINAR-L3: Argumentation Assistant
The CAMINAR-L3 module is a groundbreaking tool designed to enhance the quality and depth of legislative debates by providing argumentation assistance tailored to various political biases. The primary purpose of this module is to support Members of Congress by generating arguments that align with specific political stances, whether conservative, liberal, or somewhere in between. This functionality ensures that discussions and legislative proposals are well-rounded and consider multiple perspectives, thereby enriching the legislative process.
Image 2: CAMINAR-L3
This is achieved through a sophisticated understanding of legislative information, enabling the assistant to produce arguments that resonate with the intended legislative position. The key features of CAMINAR-L3 include its ability to customise arguments based on the user's specified political stance and its capacity to provide thorough, well-researched points that can be used in debates and legislative proposals.
One of the standout features of CAMINAR-L3 is its ability to generate arguments that reflect a specific political perspective. Members of Congress can specify whether they need arguments that lean conservative, liberal, or another stance, and the assistant will provide points that align with that ideology. This customization is crucial in legislative debates, where different political viewpoints need to be represented and considered. The assistant ensures that each argument is not only aligned with the chosen political bias but is also grounded in legal and factual accuracy, enhancing the credibility of the debate.
In practical terms, CAMINAR-L3 is used extensively by Members of Congress and their aides during the preparation and execution of debates and legislative drafting. By providing well-structured arguments that reflect the desired political bias, the assistant aids Members of Congress in formulating their points more effectively. This is particularly useful in high-stakes debates where the quality and persuasiveness of arguments can significantly influence the outcome. To ensure factual and legal accuracy, the system limits the domain of information it accesses to verified legal sources. All AI-generated content undergoes validation by legal experts, whose feedback is systematically incorporated into the system, improving the precision and relevance of future outputs.
The impact of CAMINAR-L3 on the legislative process is substantial. By ensuring that debates are enriched with well-researched and politically aligned arguments, the assistant contributes to more informed and balanced legislative discussions. This not only improves the quality of the debates but also enhances the overall legislative process by ensuring that all viewpoints are adequately considered. Moreover, the ability to generate arguments that are politically aligned helps in fostering a more dynamic and representative legislative environment, where different ideologies can be effectively articulated and debated.
CAMINAR-L4: Legislative Tracking Assistant
CAMINAR-L4 is designed to enhance the legislative operations by providing comprehensive tracking of similar bills within the legislative process. This tool addresses a critical need in legislative operations, ensuring that lawmakers are informed about the status of current bills in relation to existing or past legislation.
The primary purpose of CAMINAR-L4 is to track and compare current bills with those that are either already in the legislative process or have been processed in the past. This feature is essential for promoting legislative efficiency, as it helps Members of Congress identify redundant or conflicting bills early in the legislative process. The system periodically vectorises all bills in progress within Congress. Semantic searches are then conducted using the AI model to compare these vectorised bills, identifying similarities and ensuring that redundant or conflicting legislation is flagged. By doing so, CAMINAR-L4 aids in avoiding unnecessary duplication of efforts and ensures coherence in the legislative agenda.
One of the key features of CAMINAR-L4 is its ability to perform detailed comparisons of current bills with existing or historical legislation. This comparison capability is not limited to the text of the bills but extends to their thematic content, legislative intent, and potential implications. The system leverages advanced algorithms to identify similarities and differences, providing Members of Congress with a clear understanding of how a proposed bill aligns or conflicts with the legislative corpus. The ChatGPT-4o model, along with its default features, was used for thematic content analysis.
This information empowers Members of Congress to make informed decisions about whether to proceed with the bill, amend it to resolve conflicts, or collaborate with colleagues to consolidate similar efforts. The impact of CAMINAR-L4 on the legislative process is profound. By promoting efficiency through the early identification of redundant or conflicting bills, it streamlines legislative workflows and reduces the time and resources spent on duplicative efforts. Additionally, the coherence of the legislative framework is enhanced, as lawmakers can ensure that new bills are harmonised with existing laws. This contributes to a more organised and effective legislative process, ultimately benefiting the governance and legal landscape of Chile.
CAMINAR-L5: Regulatory Impact Assessment Assistant
CAMINAR-L5, the Regulatory Impact Assessment Assistant, is an advanced tool designed to evaluate the regulatory impact of proposed laws. The system uses prompts specifically designed for regulatory impact evaluations, with explicit instructions in the prompts about the type of analysis required. This assistant is important in ensuring that new legislative proposals are thoroughly vetted for their potential effects on the existing legal framework, enhancing the overall quality and viability of legislative outputs.
Image 3: CAMINAR-L5
Image 4: CAMINAR-L5 - User feedback mechanism
This includes a comprehensive examination of how a new bill interacts with the current body of law, identifying any potential conflicts, areas where it may complement existing laws, and gaps that it may fill. By providing a detailed impact assessment, CAMINAR-L5 ensures that new legislative initiatives are well-conceived and harmonious with the existing legal structure.
One of the standout features of CAMINAR-L5 is its ability to identify conflicts, complements, and gaps within the existing legislative framework. When a new bill is proposed, the assistant scrutinises it against the backdrop of existing laws. It highlights any conflicts where the new proposal may contradict or undermine current laws, points out how the proposal may complement or enhance the existing legal structure, and identifies gaps in the current legislation that the new bill could potentially fill. This feature ensures that Members of Congress have a clear and comprehensive understanding of the regulatory landscape they are working within. An essential feature is the determination of the hierarchy within the legal framework, which helps resolve conflicts. The model is instructed to consider the relevance of results according to the legal hierarchy. Members of Congress can use this information to refine and adjust their proposals, ensuring that the final legislative product is robust, coherent, and effective.
The impact of CAMINAR-L5 on the legislative process is substantial. By providing a thorough regulatory impact assessment, it enhances the quality of legislative proposals. Members of Congress are equipped with detailed insights that enable them to craft well-informed and technically sound laws. This not only improves the viability of the proposals but also contributes to a more cohesive and effective legislative framework. The use of CAMINAR-L5 ensures that new laws are not only innovative but also practical and aligned with the existing legal system.
CAMINAR-L6: Constitutional Support Assistant
CAMINAR-L6, the Constitutional Support Assistant, is an essential component of the Project CAMINAR suite. Its primary role is to ensure that legislative proposals comply with constitutional standards, thereby safeguarding the legal integrity of the legislative process.
Image 5: CAMINAR-L6
Image 6: CAMINAR-L6
The primary purpose of CAMINAR-L6 is to check the constitutionality of proposed bills. It meticulously reviews each legislative proposal against the constitution, ensuring that the bill adheres to the constitutional framework of the nation. This preemptive check is crucial in preventing the passage of laws that might later be deemed unconstitutional, which can save time, resources, and avoid potential legal challenges. The system ensures the constitutionality of legislative proposals by instructing the model, through specific prompt commands, to analyse the proposed text against the exclusive chapters of the Chilean Constitution. These chapters specifically define legislative matters and the powers of Congress, ensuring that the proposal is constitutionally compliant.
One of the notable features of CAMINAR-L6 is its ability to highlight the required quorums for passing specific types of legislation and to provide relevant jurisprudence. The assistant identifies whether a simple majority, a qualified majority, or a special quorum is needed for the bill in question, based on its content and implications. Furthermore, it cross-references the bill with existing jurisprudence, drawing on past judicial decisions that may impact the interpretation and implementation of the proposed law. This feature ensures that Members of Congress are fully informed about the constitutional requirements and precedents relevant to their proposals. For cross-referencing proposals with existing jurisprudence, the system uses the XML versions of Chilean legal texts. These versions include unique identifiers for each legal document, allowing for precise and unequivocal references within a vectorised document.
CAMINAR-L6 is extensively used to ensure that legislative proposals comply with constitutional standards. By reducing the risk of passing unconstitutional laws, it helps maintain the legal integrity of the legislative framework. Members of Congress are equipped with the necessary constitutional insights to craft proposals that not only address the needs of the populace but also adhere to the foundational legal principles of the nation. This leads to a more robust and legally compliant legislative process, fostering public trust and confidence in the legislative body.
CAMINAR-L7: Parliamentary Debate History Assistant
CAMINAR-L7, the Parliamentary Debate History Assistant, is a crucial feature within Project CAMINAR, designed to provide historical context for legislative debates. This assistant plays an important role in enriching the legislative process by offering comprehensive access to the historical records of parliamentary debates.
By providing access to a wealth of past debates, it allows Members of Congress to understand the evolution of discussions on specific topics. This historical perspective is invaluable for crafting informed and contextually relevant legislative proposals. The historical data, including all Diarios de Sesiones from 1990 onward, are indexed and made accessible in digital format, specifically structured in XML. The XML versions of the Diarios de Sesiones allowed for the vectorisation of these documents, with the 'Speech' of each speaker being considered the minimum granular unit of information. This structuring and metadata tagging process, which has been carried out by the Office of Drafting for over a decade, ensures that these documents are properly organised for efficient retrieval and analysis.
Members of Congress can trace the development of issues over time, identify key turning points, and understand the rationale behind previous legislative decisions.
One of the standout features of CAMINAR-L7 is its ability to grant access to past debates through a sophisticated keyword search functionality. This feature allows users to quickly locate relevant debates by entering specific keywords or phrases. The assistant then retrieves all pertinent records, making it easy for Members of Congress to find and review discussions on the topics they are currently addressing. This streamlined access to historical data ensures that Members of Congress have the information they need at their fingertips, enabling them to make well-informed decisions. One of the main challenges in maintaining an updated historical record is the continuous process of structuring the Diarios de Sesiones. It is not enough to have digital documents; they must be properly structured with sufficient granularity to enable semantic searches at different levels of detail. This ongoing effort by the Office of Drafting ensures that the records remain usable for advanced AI language models and semantic search functions.
By reviewing past debates, Members of Congress can gain insights into how similar issues were handled in the past, what arguments were made, and what outcomes were achieved. This historical context can help them avoid repeating past mistakes and build on successful strategies. Additionally, understanding the evolution of discussions on specific topics can provide a clearer picture of public sentiment and the political landscape over time.
CAMINAR-L8: Legal Doctrine Assistant
CAMINAR-L8, the Legal Doctrine Assistant, is designed to bolster the legislative process by offering comprehensive access to existing legal doctrines. This assistant significantly enriches the legislative framework by providing Members of Congress with in-depth legal insights, ensuring that legislative proposals are well-founded and robust.
The primary purpose of CAMINAR-L8 is to offer Members of Congress access to existing legal doctrines on specific topics. Searches are primarily tailored to relevant Constitutional Court rulings by adjusting specific prompts and applying filters to the associated metadata. By providing a wealth of legal knowledge, this assistant aids in the development of legislative proposals that are deeply rooted in established legal principles and precedents.
One of the standout features of CAMINAR-L8 is its comprehensive database of legal doctrines, starting with constitutional law. This database is meticulously curated to include a wide array of legal doctrines, ensuring that Members of Congress have access to the most relevant and up-to-date legal information. The focus on constitutional law ensures that legislative proposals are developed with a solid understanding of constitutional principles, helping to safeguard the legal integrity of new laws.
In practical usage, CAMINAR-L8 serves as an indispensable tool for Members of Congress during the drafting of legislative proposals. By consulting the extensive database of legal doctrines, Members of Congress can ensure that their proposals are not only legally sound but also align with established legal principles. This alignment is crucial for the coherence and stability of the legal system, as it helps prevent conflicts and inconsistencies between new and existing laws.
CAMINAR-L9: Management of Budgetary Amendments Assistant
The Management of Budgetary Amendments assistant, designated as CAMINAR-L9, is a crucial module within the CAMINAR-L suite, specifically developed to address the intricate process of handling budgetary amendments within the Chilean Chamber of Deputies. This tool is designed to streamline the amendment process, ensuring that proposed modifications to the national budget are managed efficiently and in compliance with the legal framework governing public finance.
Image 7: CAMINAR-L9
Image 8: CAMINAR-L9
The primary purpose of CAMINAR-L9 is to provide a comprehensive overview and real-time tracking of budgetary amendments. Members of Congress frequently propose changes to the budget during legislative sessions, and these amendments can range from minor reallocations of funds to significant policy shifts. The challenge lies in managing these proposals in a way that ensures transparency, adherence to legal norms, and coherence with the overall budgetary goals. CAMINAR-L9 automates the process of reviewing, categorising, and tracking these amendments, thus reducing the administrative burden on legislative staff and providing Members of Congress with instant feedback on the feasibility and implications of their proposals.
One of the standout features of CAMINAR-L9 is its ability to integrate proposed amendments directly into the existing budget proposal framework, highlighting areas of conflict or redundancy. This functionality helps Members of Congress and their aides quickly identify where amendments may overlap with other proposals or existing budgetary allocations, ensuring that resources are not double-counted or misallocated. CAMINAR-L9 also provides real-time feedback on the impact of amendments, alerting users to potential violations of constitutional or regulatory norms governing budgetary practices.
In practical usage, CAMINAR-L9 has reduced the time required to process amendments and has improved the accuracy of budgetary decisions.
IV. CAMINAR-A
CAMINAR-A1: The Parliamentary Assignments Regulation Assistant
The Parliamentary Assignments Regulation Assistant is a module within the CAMINAR-A system. It plays an important role in the administration of parliamentary expenditures within the Chamber of Deputies of Chile. This advanced tool addresses the complex regulatory framework governing how parliamentary resources are allocated and spent, ensuring that expenditures adhere to the stringent rules set forth by the institution.
The Chamber of Deputies of Chile, like many legislative bodies, must navigate a labyrinth of rules and regulations that dictate how public funds can be utilised to support parliamentary functions. These expenditures, which range from salaries for support staff to operational costs such as office rentals and travel, are subject to strict oversight to maintain public trust and ensure that resources are used efficiently and appropriately. The system limits its search domain to the specific regulations governing parliamentary expenses, ensuring responses are based solely on concrete data. Structured versions of documents and regulations were created to represent the hierarchy and relationships that were not adequately captured in the original documents. The Parliamentary Assignments Regulation Assistant was developed to assist the Chamber in this challenging task by providing accurate, timely, and contextually relevant guidance on the permissibility of various expenses.
This assistant operates through the integration of advanced artificial intelligence technologies, including natural language processing (NLP) from ChatGPT4o. These technologies allow the assistant to comprehend and respond to queries posed in natural language, reflecting the diverse ways in which users may frame their questions. The system primarily uses ChatGPT to ensure accurate and contextually relevant responses. When a member of the Chamber of Deputies or their staff submits a query regarding the appropriateness of a particular expense, the assistant quickly references the relevant sections of the Chamber's regulations and official resolutions to provide a definitive answer.
The traditional process of determining whether an expense complies with the Chamber's regulations often required extensive manual effort, involving the consultation of numerous legal texts and, at times, multiple levels of bureaucratic approval. This not only slowed down the decision-making process but also introduced the potential for errors and inconsistencies in the application of the rules. The Parliamentary Assignments Regulation Assistant effectively mitigates these issues by automating the interpretation of the Chamber’s regulations, ensuring that responses are both swift and accurate.
The introduction of this module is part of a broader effort within the Chilean Chamber of Deputies to leverage digital tools to enhance its governance. The assistant is not merely a reactive tool but also serves a proactive role in promoting adherence to the institution’s regulations. By providing instant clarification on what constitutes an allowable expense, it helps to prevent unintentional violations of the rules, thereby safeguarding the Chamber against potential misuse of funds and enhancing its overall operational integrity.
The Parliamentary Assignments Regulation Assistant also reflects the Chamber of Deputies' commitment to transparency. By ensuring that all expenditures are rigorously checked against established regulations, the assistant contributes to the institution’s broader goals of accountability and public trust. This transparency is further supported by the assistant’s integration with other modules within the CAMINAR-A system, creating a comprehensive digital ecosystem that supports the Chamber’s administrative and legislative functions.
CAMINAR - A2: The Online Data Assistant for Parliamentary Assignments
The Online Data Assistant for Parliamentary Assignments, a module within CAMINAR-A, is essential to the real-time management of parliamentary expenditures in the Chilean Chamber of Deputies. This tool provides instant access to specific data regarding parliamentary spending, facilitating a more dynamic and accurate approach to overseeing financial resources. The system manages real-time access to parliamentary expenditure data by using a natural language model that classifies the type of question asked. Based on the classification, it internally calls different WebAPIs to retrieve the specific data in real-time.
The assistant is designed to respond to queries about the current status of various parliamentary expenses, such as fuel consumption or office rentals. When a Member of Congress or staff member inputs a request for information, the assistant immediately retrieves the relevant data from the Chamber’s database. This allows users to obtain precise figures and detailed reports on their expenditures, without the need for manual data retrieval.
The assistant's capacity to deliver real-time data has transformed the way financial information is accessed and utilised within the Chamber. By automating the process of data retrieval, it ensures that users have the most current information available, enabling them to make informed decisions based on up-to-date figures. This has reduced the time required to gather and analyse financial data, making the management of parliamentary assignments more efficient. The assistant integrates with the same methods used by CAMINAR A1, ensuring that the data provided is both accurate and up-to-date. The main challenge in maintaining accuracy is ensuring that the language model correctly interprets and classifies the questions, aligning them with predefined methods that can return the appropriate response.
Furthermore, the Online Data Assistant is capable of handling a range of specific inquiries, offering detailed insights into particular aspects of parliamentary spending. For example, it can provide exact amounts related to specific expenses or offer a summary of financial activities over a given period. This functionality is crucial for maintaining accurate records and ensuring that parliamentary resources are being utilised effectively.
The assistant is also a part of a broader initiative within the Chamber to improve the transparency and accountability of parliamentary operations. By making financial data readily accessible, it contributes to a more open and accountable system of governance, where expenditures can be monitored and reviewed with greater ease.
CAMINAR - A3: The Receipt Information Extraction Assistant
The Receipt Information Extraction Assistant, another critical module within the CAMINAR-A system, is designed to streamline the process of managing and verifying parliamentary expenditures in the Chilean Chamber of Deputies. This assistant focuses specifically on the extraction and validation of information from receipts and other financial documents submitted by parliamentarians as part of their expense reporting.
In the implementation of CAMINAR-A3, various models such as Anthropic's Claude 3.5, OpenAI's GPT-4, and Google's Gemini have been tested for their ability to extract and validate information from the diverse formats of receipts.
The assistant automates the extraction of essential details from various types of receipts, such as the document type, date, amount, and other relevant financial data. By doing so, it alleviates the need for manual entry and reduces the potential for human error in the processing of these documents. When a receipt is submitted, the assistant analyses the document, identifies the key information required for the expense report, and accurately extracts this data.
Currently, the system is undergoing validation, where comprehensive tests are being conducted to assess the accuracy of these models, taking into account the specific types of documents and unique characteristics of the receipts presented by Members of Parliament.
One of the distinguishing features of the Receipt Information Extraction Assistant is its ability to handle different formats of financial documents. Whether the receipt is a standard invoice or a more complex document, the assistant is trained to recognise and process the necessary information efficiently. This capability ensures that even when documents vary in their layout or presentation, the assistant can reliably extract the required data.
The extracted information is then validated against the Chamber’s existing financial records to ensure compliance with the established regulations. This validation process is crucial in maintaining the integrity of parliamentary expenditures, as it helps to identify discrepancies or errors that may arise during the submission of expense reports. By automatically cross-referencing the extracted data with the Chamber’s records, the assistant plays a key role in ensuring that all reported expenses are accurate and justified.
In addition to its extraction and validation functions, the assistant also supports the broader goal of enhancing the transparency and accountability of parliamentary spending. By providing a systematic and automated approach to managing receipts, the assistant contributes to a more efficient and transparent financial reporting process within the Chamber.
V. Principles Guiding CAMINAR-L
The CAMINAR-L project is driven by key principles that underpin its functionality and ensure its effectiveness in supporting the legislative processes of the Chilean Congress. These principles are crucial for maintaining the integrity, accuracy, and fairness of the legislative assistants, thereby enhancing the overall quality of legislative work.
The foundation of CAMINAR-L lies in its use of vectorised legal databases. This approach transforms complex legal texts into a structured format that allows for efficient processing and retrieval by AI algorithms. The transformation ensures that the system works with comprehensive and contextually relevant data, capturing the full scope of Chile’s legal framework, from the Constitution to specific regulatory norms. This meticulous structuring is vital for providing precise and tailored information to Members of Congress, facilitating well-informed decision-making and enhancing the legislative process.
Human validation is another cornerstone of CAMINAR-L. Despite the sophistication of AI, the role of human oversight cannot be overstated. Human validators play a critical role in reviewing and verifying the information generated by the AI, ensuring that the outputs are accurate and contextually appropriate. This process not only reduces the risk of errors but also ensures that the recommendations and insights provided to Members of Congress are aligned with the legislative context. The blend of AI efficiency with human expertise helps maintain high standards of reliability and trust in the system.
The regulation of bias within CAMINAR-L is a fundamental principle aimed at ensuring fairness and balance in the system’s outputs. Some applications within CAMINAR-L are designed to operate without bias, while others incorporate a controlled level of bias to reflect the specific needs and perspectives of users. This careful modulation of bias prevents the reinforcement of existing prejudices and promotes a more equitable legislative process. By managing bias effectively, CAMINAR-L supports objective and impartial decision-making, ensuring that the legislative recommendations provided are fair and balanced.
The principle of normative hierarchy is essential for prioritising the most important legal norms in the responses generated by CAMINAR-L. The system is designed to consult the highest-ranking legal norms first, beginning with the Constitution, followed by statutory laws, regulations, and other relevant legal texts. This approach ensures that the legislative advice provided is grounded in the most authoritative and relevant legal sources, supporting the creation of coherent and legally sound legislative proposals.
Complementing these principles is a dedicated focus on refining the prompts used to interact with the AI assistants. This role, often referred to as the 'prompt engineer' or 'prompt manager,' involves continuous analysis and improvement of the questions posed to the AI, ensuring that the system provides the most accurate and relevant information possible.
These guiding principles of vectorized legal databases, human validation, bias regulation, and normative hierarchy are integral to the functioning of CAMINAR-L. They ensure that the system provides accurate, reliable, and fair support to the legislative processes of the Chilean Congress, thereby enhancing the quality and efficiency of legislative work. Through these principles, CAMINAR-L embodies a commitment to innovation, integrity, and excellence in legislative assistance.
VI. The Impact and Transformation of CAMINAR
The CAMINAR project represents a watershed in the evolution of legislative and administrative functions within the Chamber of Deputies of Chile. This initiative has fundamentally redefined how the Chamber operates by integrating advanced AI-driven tools and digital technologies into its core processes. CAMINAR's implementation signals a decisive shift towards a more dynamic, data-driven legislative operations where decisions are informed by real-time insights, and administrative tasks are streamlined through automation.
The CAMINAR-L system offers significant benefits to the legislative process within the Chilean Chamber of Deputies, primarily through enhancing efficiency and demonstrating a commitment to modernisation and technological innovation. Each module within CAMINAR-L plays a crucial role in achieving these objectives, contributing to a more streamlined, accurate, and responsive legislative environment.
These principles ensure that the system provides accurate, reliable, and fair support to Members of Congress, enhancing the overall quality and efficiency of legislative work. By combining AI efficiency with human oversight, CAMINAR-L maintains high standards of reliability and trust, ensuring that legislative processes are both innovative and grounded in robust legal principles.
Innovation is another critical benefit of CAMINAR-L, demonstrating the Chamber of Deputies' commitment to leveraging modern technology within the traditional legislative process. The integration of advanced digital technologies and artificial intelligence in CAMINAR-L showcases the Chamber's forward-thinking approach to legislative work. By adopting these cutting-edge tools, the Chamber not only modernises its processes but also sets a precedent for other Parliaments.
Complementing these advancements in legislative processes, CAMINAR-A extends the same commitment to modernisation and efficiency to the administrative functions of the Chilean Chamber of Deputies. CAMINAR-A enhances the management of parliamentary assignments and expenditures through the use of artificial intelligence, ensuring that these processes are carried out with precision, transparency, and accountability. By automating key administrative tasks, CAMINAR-A not only reduces the potential for human error but also improves the speed and accuracy with which financial data is processed and validated.
The integration of CAMINAR-A into the Chamber’s operations underscores the institution's dedication to comprehensive digital transformation. Just as CAMINAR-L sets new standards for legislative efficiency, CAMINAR-A represents a significant leap forward in the administrative domain, ensuring that the Chamber’s financial management is both modern and robust. This holistic approach to digital innovation positions the Chilean Chamber of Deputies as a leader in the adoption of technology across all facets of parliamentary work.
The innovative nature of CAMINAR lies not just in its current capabilities but also in its adaptability and potential for future growth. The Chamber's commitment to continually refining and expanding the system ensures that it will remain a cutting-edge tool for legislative support for years to come.
Together, CAMINAR-L and CAMINAR-A demonstrate the Chamber of Deputies' comprehensive strategy to enhance both legislative and administrative operations through the adoption of advanced technologies. This dual approach not only improves the efficiency and reliability of parliamentary functions but also reinforces the Chamber’s commitment to transparency, accountability, and innovation in public governance.
VII. System Architecture and Design
The architecture and design of the CAMINAR system, encompassing both CAMINAR-L (Legislative) and CAMINAR-A (Administrative), represent a sophisticated technological framework, designed to support the complex operational needs of the Chamber of Deputies.
CAMINAR is built upon a tiered architecture that consists of distinct layers, each responsible for a specific set of functions within the broader system:
Application Layer: This layer comprises the servers hosting the various tools and interfaces used by the Chamber. This includes internally hosted servers using technologies such as Python and Microsoft Semantic Kernel to support the operation of various tools and applications.
Data Layer: At this level, the Oracle database servers, which are internally housed, manage the vast array of legislative and administrative data.
AI Service Layer: CAMINAR leverages a combination of cloud-based AI services hosted in the cloud, such as the Pinecone vector database and OpenAI language models, while others, including Whisper for transcription, are hosted on dedicated internal servers.
Central to CAMINAR’s operation is its robust data infrastructure, which forms the second layer of the system. Data management within CAMINAR is underpinned by Oracle database servers, housed internally to ensure the integrity and security of the Chamber’s legislative and administrative records. The databases utilised by CAMINAR are not merely repositories of information but have undergone extensive validation, cleansing, and vectorisation processes. This pre-processing of data ensures that the AI models deployed within CAMINAR can retrieve, analyse, and present relevant information with high precision.
The third layer of CAMINAR’s architecture is dedicated to AI services. This layer is distinctive in that it incorporates both cloud-based and locally hosted AI models. For the generative AI models that underpin much of CAMINAR’s functionality, such as real-time transcription and natural language processing, the system utilises ChatGPT Enterprise. For general tasks, OpenAI's models have been primarily used, including GPT-3.5 turbo, GPT-4, GPT-4o, and Whisper large-v3. These models were chosen after rigorous testing due to their superior performance, speed, and response quality in solving real-world problems. Additionally, Anthropic's Claude 3.5 has been utilised for certain specific tasks.
However, not all AI processes within CAMINAR are cloud-dependent. In cases where data sensitivity or regulatory compliance dictates the need for local processing, dedicated internal servers host the necessary AI services. These internal servers ensure that critical data never leaves the Chamber’s control, maintaining compliance with Chilean legal frameworks governing data privacy and security. The strategic decision to use both cloud and internal servers reflects a balance between leveraging the expansive computational resources of cloud-based AI and the need for stringent data governance in sensitive parliamentary environments.
The multi-layered structure of CAMINAR, combining AI services, data management, and application interfaces, allows the Chamber of Deputies to manage vast quantities of legislative and administrative data with precision and agility.
VIII. Development Cycle
The development cycle of the CAMINAR project was marked by a robust focus on research, innovation, and iterative refinement. The team adopted a methodical approach that emphasised experimentation and exploration with various AI models, tools, and services, all while addressing the specific challenges faced by the Chamber of Deputies. This research-intensive process allowed for a comprehensive evaluation of the available technologies, with each phase designed to test, validate, and refine the AI functionalities before their integration into the existing parliamentary systems.
The development process began with an extensive research and experimentation phase, wherein the technical team conducted a series of Proof of Concept (PoC) trials. These trials were essential in identifying viable solutions while discarding options that did not meet the project’s requirements. The PoC phase was intensive, requiring rigorous testing of each model and tool, with end users actively involved through the use of demonstration versions (demos). These demos were invaluable in ensuring that the outputs generated by the AI models were accurate, reliable, and aligned with the Chamber’s operational needs.
User participation, particularly from the Chamber’s staff, was essential during this phase. The active engagement of final users in the demo trials ensured that their feedback directly informed the refinement of the AI functionalities. This early-stage validation process provided crucial insights, allowing for the adjustments and fine-tuning of the AI outputs. Once the demos were successfully validated, the functionalities were integrated into the Chamber's existing systems using a classic software development process. This method ensured a smooth transition from experimental phases to full-scale deployment within the legislative and administrative frameworks of the Chamber.
An iterative approach defined the broader development cycle, incorporating continuous loops of research, development, testing, and validation. These short iterations allowed the team to rapidly discard unviable options while identifying the potential strengths of the tested solutions. Each iteration was geared towards incremental improvements, with constant feedback loops from the demos, ensuring that the AI functionalities were optimised for the specific needs of the Chamber.
Collaboration between the technical team and legal experts, Members of Congress, and other key stakeholders within the Chamber was a cornerstone of the development process. It was imperative that the AI tools being developed accurately reflected the legal and procedural frameworks of the Chamber. To this end, the technical team worked closely with domain experts from the outset, ensuring that the AI functionalities were properly aligned with the unique requirements of legislative work.
Early involvement of key figures, such as the Secretary General and legislative lawyers, was instrumental in validating the PoC trials and demos. These experts played a crucial role in the selection and refinement of the data sets that powered the AI models. Their contributions were essential in adjusting the prompts used by the AI and ensuring that the results generated during each stage of development were legally sound and contextually appropriate. This collaboration extended through all phases of the development cycle, ensuring that the outputs of the AI systems were continuously validated against the Chamber’s legal and operational standards.
IX. Data Management
The data management process within CAMINAR, particularly for CAMINAR-L (Legislative) and CAMINAR-A (Administrative), revolves around the efficient handling and vectorisation of legal databases. A key factor that facilitated the integration of AI into the system was the pre-existing availability of Chile’s complete legal database within the Chamber of Deputies. This database, which includes enacted laws, regulations, legal decrees, and bills, was stored in XML format prior to the development of CAMINAR.
The fact that all legislative documentation was already in XML format proved crucial to the process of vectorisation. This structured format provided the necessary granularity for the AI models employed in CAMINAR to interpret the legal texts with a high degree of accuracy. The vectorisation process involved converting these detailed XML documents into a format that could be efficiently processed by the language models, ensuring that they could retrieve, analyse, and respond to complex legal queries in a precise manner.
X. Navigating the Political Landscape: Securing Buy-In for CAMINAR
The development of CAMINAR, with its innovative integration of AI into the core functions of the Chilean Chamber of Deputies, represents a significant technological achievement. However, the true measure of its success lies not just in its technical prowess, but also in its ability to seamlessly integrate into the political reality of the legislative process. This necessitates navigating the complex landscape of political will, ensuring buy-in from key stakeholders, and ultimately, achieving institutional acceptance of these transformative tools.
According to the Secretary-General of the Chamber of Deputies of Chile, Mr. Miguel Landeros, "The technical work is the fastest. The political decision is the most difficult, although in our case, both processes were carried out expeditiously."
This highlights a fundamental truth: technological innovation, while crucial, must be accompanied by the political will to embrace change and adapt existing structures. In the context of CAMINAR, securing this political buy-in was essential for different reasons.
Firstly, the implementation of CAMINAR necessitates modifications to the Chamber's internal regulations and operating procedures. Addressing these concerns requires open dialogue, transparency about the intended benefits of CAMINAR, and a willingness to address concerns raised by Members of Congress.
Secondly, the adoption of AI-powered tools in a traditionally human-driven domain like Parliaments can raise questions about the potential displacement of human expertise and the impact on the roles of legislative staff. It is crucial to communicate that CAMINAR is designed to augment, not replace, human judgement. By framing CAMINAR as a tool that empowers rather than displaces, the Chamber can foster a more receptive environment for its integration.
Thirdly, the success of CAMINAR relies heavily on the active participation and engagement of Members of Congress. This necessitates addressing potential apprehensions about the use of AI, ensuring that the tools are user-friendly and intuitive, and providing adequate training and support to familiarise Members with the functionalities of CAMINAR. Building trust in the system's reliability, accuracy, and ability to enhance their legislative work is paramount.
Securing political will also involves addressing potential concerns about transparency and accountability. These concerns are not hypothetical, as demonstrated by questions raised about the potential for CAMINAR to reveal sensitive information, such as the salaries of public officials, requiring a careful balance between transparency goals and data privacy considerations. Demonstrating how CAMINAR strengthens these principles, for example, by providing clear audit trails of its recommendations and ensuring human oversight at critical stages, can help alleviate any reservations.
Ultimately, achieving institutional acceptance of CAMINAR required a multi-pronged approach that combined clear communication, collaborative implementation, and demonstration of value. Transparent and consistent communication with Members of Congress about the goals, benefits, and potential challenges of CAMINAR was essential. Involving Members and staff in the implementation process, soliciting their feedback, and incorporating their suggestions can foster a sense of ownership and reduce resistance to change. Providing concrete examples of how CAMINAR enhances legislative efficiency, improves the quality of legislative proposals, and strengthens transparency can build confidence and encourage adoption.
The Chilean Chamber of Deputies' success in navigating these political considerations will ultimately determine the long-term impact of CAMINAR. By securing buy-in from key stakeholders and fostering a culture of openness to technological innovation, the Chamber can solidify CAMINAR's position as a transformative force within the legislative process.
XI. User Feedback and Human Validation
The implementation of CAMINAR was driven by the continuous feedback and involvement of users. This process was marked by distinct challenges, particularly in the context of research, evaluation, and human validation. The process of identifying the best available options to address each specific problem required continuous investigation and iteration. As various cloud-based models underwent frequent updates within short periods, the team found it necessary to constantly re-evaluate and test the effectiveness of these models for each use case. This dynamic environment of evolving AI technologies demanded a sustained commitment to research and refinement, ensuring that the tools remained adaptable and effective.
One of the principal challenges encountered during the implementation phase was the engagement of everyday users to validate the tools and provide constructive feedback. Ensuring that non-expert users could interact meaningfully with the AI-driven assistants, and then contribute valuable insights to refine and enhance the solutions, proved to be a complex task. The process of gathering feedback from this user base, while essential to improving the system, involved overcoming initial hesitations and facilitating a thorough understanding of how the tools could be most effectively utilised. Nonetheless, this engagement was crucial for ensuring that CAMINAR remained user-centric and responsive to real-world legislative needs.
Future improvements to CAMINAR services are closely informed by this ongoing feedback process. Looking forward, several enhancements are planned. One of the key areas under development is the automatic recognition and identification of Members of Parliament in video recordings. This feature is intended to complement the existing automated transcription of plenary and committee debates by adding the names of speakers to the transcripts without manual intervention. The integration of this functionality would streamline the documentation of legislative proceedings, ensuring that each contribution is accurately attributed in real-time.
Additionally, there are concerted efforts to expand the range of outputs generated by AI tools, particularly in the production of simplified summaries of legislative texts. These summaries are being designed with the general public in mind, using accessible language that makes complex legislative information easier for non-expert citizens to understand. By improving the accessibility of legislative documents, the Chamber aims to enhance public engagement with the legislative process, reinforcing transparency and accountability.
In parallel, ongoing tests are being conducted on local servers that have been specifically designed for the implementation of models that do not depend on external services. This shift to locally hosted models is intended to address certain specific challenges, providing a more secure and adaptable solution that can be tailored to the unique requirements of the Chamber. This approach also reflects a broader strategy to ensure that sensitive data remains under the Chamber's control, in line with the stringent regulations governing parliamentary operations.
A key aspect of the CAMINAR system is the robust process of human validation that underpins each AI-generated output. Every interaction with the AI assistants, whether in the form of a query or a response, is subject to mandatory human oversight. This validation process is systematically recorded, with each interaction logged and the outcome of the human review meticulously documented. The system ensures that every piece of information generated by the AI is verified by a human expert before being finalised. Moreover, the identity of the individual responsible for the validation is recorded, ensuring accountability and providing an additional layer of reliability. This structured validation process guarantees that while AI serves to enhance the speed and efficiency of the legislative process, it does not replace the critical judgement and oversight provided by human expertise.
XII. Conclusion
The transformation of the Chamber of Deputies of Chile through the CAMINAR project highlights the profound impact that artificial intelligence can have on legislative and administrative processes. More than just a shift from paper to digital, CAMINAR represents a rethinking of how parliaments can function in the future. By leveraging AI for tasks like legal research, transcription, and financial oversight, the Chamber has demonstrated that efficiency, transparency, and accountability are not only achievable but can be significantly enhanced through strategic technological investment.
However, the success of CAMINAR lies not only in its technological capabilities but also in the Chamber’s ability to navigate institutional and political complexities. The project's effectiveness was contingent on securing buy-in from key stakeholders, managing concerns about AI’s role in legislative work, and maintaining the balance between automation and human oversight. This speaks to a broader lesson: the success of technological innovation in parliaments is as much about leadership and institutional will as it is about the tools themselves.
The Chamber’s experience with CAMINAR highlights that digital transformation is not a one-time shift but an ongoing process. The system’s adaptability to evolving legislative needs and emerging AI technologies will determine its long-term value.